Accuracy, availability, and traceability of company assets are key to operational efficiency and financial integrity. Being able to quickly find and verify each asset leads to better physical asset management. This is exactly why asset tagging and proper asset management are so essential for businesses..
Implementing asset tagging solutions—from barcodes to advanced RFID systems—improves asset visibility. It helps reduce human error and supports compliance with audit and regulatory requirements. A recent Gartner survey revealed that 18% of accountants make financial errors daily, while over half make several mistakes each month. By streamlining identification, tracking, and management, asset tagging minimizes the need for manual record-keeping.
This guide explores best practices for asset tagging and highlights available tagging technologies. It walks through key implementation steps, essential considerations, and the benefits of a solid tagging strategy. When done right, asset tagging improves lifecycle management, increases productivity, and lowers the risk of asset loss or theft. Let’s dive in
What is Asset Tagging?
Asset tagging assigns a unique identifier to each physical asset using labels like barcodes, QR codes, or RFID tags for seamless tracking. These tags link directly to asset register records, ensuring accurate, up-to-date data. By scanning a tag with an asset tagging system, organizations can quickly identify and manage assets throughout their lifecycle—reducing errors, losses, and theft.
Moreover, employees can instantly access or update asset information simply by scanning a tag. This streamlined process boosts both accuracy and efficiency, especially when managing assets like laptops, vehicles, or machinery. As a result, asset tracking becomes faster, more reliable, and easier to maintain.
Asset tagging plays a critical role in controlling physical inventory—here’s why it’s important.
Why Asset Tagging Matters (Benefits)
Asset tagging delivers powerful benefits:
Accurate Identification:
Unique tag codes prevent duplicate records. Every asset has one ID in the system. This single ID eliminates confusion across departments.
Reduces loss and theft:
Asset tracking cuts asset loss by up to 50%. This saves companies hundreds of thousands of dollars on replacements.
Boosts asset utilization:
Tracking can raise utilization rates 10–20%. It reveals underused items and prevents unnecessary purchases.
Speeds asset searches:
Companies cut search time by up to 90%. Staff spend fewer hours hunting for tools or inventory.
Accelerates audits:
Automated scanning yields faster, more accurate inventories. This saves time and reduces human error during audits.
Improves security.
Tagged assets are easily located if moved or stolen. Asset history ensures accountability for every item.
Enhances compliance:
Detailed tag logs support financial audits and regulatory checks. You always know each asset’s status.
Delivers ROI:
Many organizations find tagging systems pay off in 1–2 years. Lower labor costs and fewer losses often outweigh initial investment.
Asset tags drive efficiency and control. They cut manual work, reduce losses, and ensure reliable audits. By making asset data instantly available, tags empower managers to make informed decisions.
Key Asset Tagging Technologies
Modern asset tagging uses various labels and tech, each suited to different needs:
Barcode Labels:
Low-cost, line-of-sight tags printed with machine-readable codes. A barcode sticker on each item allows rapid inventory scans. Barcodes work well on boxes, shelves or office gear, and can hold thousands of characters in 2D form.
QR Code Tags:
Quick Response (QR) codes are 2D matrix tags scannable by smartphones. You can store more data (URLs, manuals) than a simple barcode. Field workers can tap a QR tag with a phone to instantly view equipment instructions or history.
RFID Tags:
RFID tags contain embedded chips and antennas. They’re either passive (no battery) or active (with battery). Active tags broadcast constantly, while passive ones respond when energized by a reader. RFID allows contactless scans without direct visibility. It’s ideal for bulk items or hard-to-reach assets. Advanced systems can boost inventory accuracy by 65–99%. For a deeper dive into how RFID improves accuracy and scan speed, see our full guide on RFID asset tracking.
Bluetooth (BLE) Beacons:
BLE trackers use Bluetooth Low Energy for real-time indoor tracking. They’re power-efficient, with batteries that last years, and work well in complex spaces like hospitals or warehouses. Assets can be located by pinging nearby receivers—no full WiFi needed.
NFC Tags:
Near-Field Communication tags can be read by tapping with a smartphone. NFC is handy for on-the-spot asset checks or maintenance logs. For example, a technician taps an NFC tag on a machine to log a repair. NFC tags are cheap and useful for device-centric workflows.
IoT & GPS Trackers:
For remote sites or assets in transit, GPS or IoT trackers work best. These active tags send location data via cellular or LoRa networks. With geo-tagging, you can track the asset’s last known location anytime.
Each technology fits different use cases. Often companies combine them (e.g. barcodes for desk items, RFID for pallets, GPS for vehicles). The key is every tag has a unique asset ID that links to the same system. This unified ID is the single source of truth that all departments use.
Challenges and Considerations in Asset Tagging Implementation
Implementing asset tagging brings major benefits but requires careful planning. Addressing key challenges proactively ensures a smooth and successful rollout. Below are essential considerations for effective asset tagging and management:
Availability of Accurate Asset Data
An accurate asset register is essential before starting asset tagging. Incomplete or inaccurate records initially cause confusion and errors during implementation. Issues like duplicate entries or unlisted assets complicate the tagging process. Clean and verify your asset data first to ensure successful implementation.
Choosing the Right Tagging Technology (Barcode vs. RFID)
Choosing the right tagging technology hinges on your specific needs and budget. Barcode tags are affordable and simple to create. However, they need direct line-of-sight scanning. On the other hand, RFID tags are more advanced. They allow scanning assets without direct visibility.
Choosing Durable Asset Tags
Selecting durable tags is crucial for your assets’ environments. Consider tag materials based on exposure to harsh conditions. Durable tags maintain readability over time. This ensures your asset tagging solution remains effective long-term. Explore the different types of asset tracking tags and which are best for different environments.
Selecting the Right Asset Tagging Services Provider
Evaluate asset tagging services by considering their geographic reach and industry expertise. Additionally, assess their capabilities in creating asset baselines and managing reconciliation. Then, examine their available asset tags and their experience with similar companies. Ultimately, a proven provider ensures smooth implementation and ongoing support.
Choosing the Best Asset Tagging Software
Choosing the right asset tagging software means matching features to your specific requirements. Look for mobile applications, automation, reporting analytics, and user-friendly interfaces. Additionally, check for integration compatibility. Effective software simplifies asset management, reduces errors, and boosts efficienc
Maintenance of Tags and Data
Regular maintenance of asset tags and data ensures continued effectiveness. Tags can deteriorate, becoming damaged or unreadable. Therefore, establish routine inspections during regular audits. Replace worn or missing tags promptly. Consistent maintenance protects asset data accuracy and reliability.
By addressing these key considerations upfront—accurate data, suitable technologies, durable tags, quality service providers, effective software, and regular maintenance—your asset tagging implementation will be effective and sustainable.
Implementing Asset Tagging: Step-by-Step
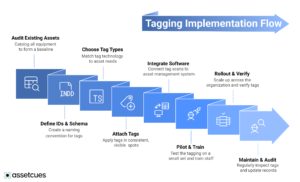
To deploy tagging effectively, follow a clear process:
Audit existing assets
type, value, location) to form a baseline. Cleanse duplicates and outdated records beforehand through assetcues.
Define IDs & schema
e.g. FAC-1001). Decide if tag numbers match asset IDs or are kept separate. (Tip: using generic sequential tag numbers reduces errors — see assetcues.)
Choose tag types
Match tag technology to asset needs: indoor/outdoor, range, durability. Consider future integration (ERP, IoT)
Attach tags
Apply tags in consistent, visible spots. Record each tag scan in your asset register. Mobile apps (like AssetCues mobile app) speed this process.
Integrate software
Connect tag scans to an asset management system or CMMS. AssetCues software, for example, syncs with SAP/Oracle and sends maintenance alerts.
Pilot & train
Test the tagging on a small set. Train staff on scanning and procedures. Use feedback to refine.
Rollout & verify
Scale up across the organization. Conduct a full asset verification to confirm all tags are active.
Maintain & audit
Regularly inspect tags for damage and update records. Schedule periodic audits so data stays accurate (replace missing tags immediately).
White Paper
Automate recording of asset checkin and checkout using RFID Technology.
Download our latest whitepaper to learn how to implement and benefit from automation
White Paper
Automate recording of asset checkin and checkout using RFID Technology.
Download our latest whitepaper to learn how to implement and benefit from automation
Best Practices for Tagging Implementation
Plan and Categorize:
Inventory all asset types first. Create an asset repository with categories (IT, furniture, vehicles, etc.). Assign a unique coding scheme (e.g. “NY-IT-001” for New York IT laptop) so each asset ID is meaningful. Begin by tagging high-value, mobile or heavily used assets.
Choose Durable Tags:
Selecting tags suited to the environment is key. Indoor equipment can use paper barcode labels. However, outdoor or heavy machinery needs robust tags, like metal plates or laminated labels. Rugged or tamper-evident tags prevent damage or removal. Durable tags avoid frequent replacements and ensure long-term tracking.
Standardize Tag Info:
Decide what data belongs on each tag. At minimum, include a serial number or ID. This ties back to your asset register. Many firms also add the asset name, department, or location. Avoid putting sensitive information on tags. If lost, it could aid thieves. You can encode extra data, like purchase date or warranty, in QR or RFID tags for quick reference.
Use Asset Management Software:
Implement a system or software that scans and logs each tag in real time. AssetCues’ asset management platform (for example) lets you scan with mobile devices to instantly view or update asset data. Integrating software ensures that each scan automatically updates the central database, preventing duplicate entries and errors.
Integrate with IoT/Analytics:
Where possible, connect tagging to IoT and AI tools. For example, IoT sensors on equipment can signal maintenance needs, while BLE beacons aid indoor tracking. AI-powered analytics on tag data can predict failures or optimize utilization. Modern tagging systems often feed data into dashboards for decision-making.
Train Your Team:
Ensure staff know how to use tags and scanners. Hold training sessions on how to attach tags, scan correctly, and record updates. Promote consistency by setting procedures (where to place tags, when to scan). Well-trained users help make tagging effective and keep data clean.
Audit and Update Regularly:
Perform routine checks. Periodic audits (annual or quarterly) ensure every asset’s tag matches the record. Automated tag scans greatly shorten audit time. After audits, reconcile any missing or mismatched assets. Also update tags when assets move, get repaired or retired to keep the register current.
Enforce Policies:
Have clear rules for tagging: mandate that all new assets get tagged on arrival, and no critical asset should remain untagged. Tie tagging to processes like check-in/check-out. For example, require employees to scan tags when borrowing equipment. This enforces accountability.
By following these steps, organizations ensure tagging is thorough and consistent. A systematic rollout—from planning and tagging to software integration and audits—maximizes the benefits of asset tags.
Streamline tagging. Improve audits.
Explore Fixed Asset Register and Barcode Tracking with AssetCues.
Streamline tagging. Improve audits.

Cost vs ROI of Asset Tagging
Businesses weighing asset tagging implementation typically evaluate upfront costs against ROI. Though initial expenses are involved, asset tagging consistently provides significant long-term returns. Here’s a breakdown of costs and offsetting benefits:
Upfront Costs
Initial expenses cover asset tags, hardware, and software. Tags range from basic to advanced. Hardware includes scanners and readers. Software involves licenses and integrations. External service providers may also add short-term costs.
Operational Savings
Asset tagging immediately boosts operational efficiency by significantly cutting down on manual labor. Automated tracking saves a lot of time previously spent on inventory and locating equipment. This frees employees from manual tasks, allowing them to focus on more valuable activities. Ultimately, these efficiency gains increase productivity without extra staffing costs
Loss Prevention and Asset Utilization
Asset tagging significantly boosts ROI by curbing loss, theft, and misplacement, preventing unnecessary equipment purchases. Many companies over-purchase without clear inventory data. Tagging offers visibility into available assets, avoiding duplicate buys and excess stock. This also enables optimized asset utilization across departments, reducing overall spending and waste.
Long-Term ROI
The value of asset tagging grows with scale and asset volume. Manual tracking becomes costly and inefficient as organizations expand. Many companies find asset tagging solutions pay for themselves quickly. Long-term ROI comes from saving on labor, fewer asset losses, and better decisions.
Asset tagging proves to be a wise long-term investment, combining cost-efficiency, accuracy, and improved operational control.
Conclusion
Asset tagging creates unique identification and a single source of truth for all stakeholders. Following best practices, like choosing durable tags and applying consistent IDs, improves asset visibility and control. Use IoT-enabled tags and analytics for real-time insights. With AssetCues, companies unify asset data from Finance to Maintenance. This boosts efficiency, cuts costs, and ensures assets are always found when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What should I print on an asset tag?
At minimum include a unique ID or serial number. You can encode information like asset name, department, or purchase date on the tag if desired. Many companies also add a barcode or QR code for quick scans. It’s wise not to display sensitive info (e.g. company name) on tags. Some tags even carry geolocation data or IP addresses for IoT tracking.
Q: How do passive and active asset tags differ?
Passive tags have no battery; they only respond when scanned nearby (short range). Active tags carry a battery and can broadcast signals over long distances for real-time tracking.
Q: RFID vs. barcode for asset tracking?
Barcodes/QR codes are cheap and easy to print. They require line-of-sight to scan. RFID tags (passive or active) cost more but work without line-of-sight and can be scanned in bulk. Choose based on your needs: use barcodes for basic tracking, and RFID for real-time or high-volume tracking.
Q: Can tagging assets integrate with software?
Yes. Asset tags feed data into asset management or ERP systems. For example, scanning a tag can automatically update the asset’s status in an AMS or CMMS. AssetCues supports integrations (e.g. SAP) so that every tag scan syncs instantly to the central asset register.
Q: Asset tagging or asset marking – which to use?
Asset Marking (engraving or painting IDs) is permanent but not easily scanned. Asset tagging uses barcodes/RFID for digital tracking. For full tracking and visibility, modern systems rely on asset tagging coupled with software.
Q: How does geo-tagging work for assets?
Geo-tagging means including geographic coordinates (or using GPS trackers) so you know an asset’s location. Some modern tags can store geo-location info, and IoT trackers can send live GPS data. By using asset apps or IoT sensors, you can view an asset’s position on a map. This is especially useful for vehicles, outdoor equipment or field tools, ensuring you always know where critical assets are located.
About Author





