Introduction
Asset tracking is the backbone of effective operations across industries—from IT and manufacturing to healthcare and retail. Traditionally, companies have relied on barcode systems or manual checks to monitor assets. However, these methods often fall short in terms of efficiency and reliability. RFID technology overcomes the limitations of barcode scanning by eliminating the need for a line‑of‑sight—without significant additional costs or implementation hassles. In this post, we will explore the key aspects of RFID asset tracking and explain how adopting this technology can revolutionize your asset management strategy.
What is RFID Asset Tracking?
RFID asset tracking employs radio frequency signals to automatically identify assets through small tags affixed to each item. These RFID tags store unique data that is captured by RFID readers. Unlike barcodes—which require manual scanning—RFID tags can be read remotely and simultaneously, significantly expediting physical verification and tracking processes. RFID asset tracking automatically updates asset status and location in real time. This enables organizations to maintain accurate records. It also streamlines operations and reduces the risk of lost or stolen assets.
RFID vs. Traditional Barcode Systems
Although barcode systems have long been used for asset tracking, they require a direct line of sight. Each item must be scanned individually, making the process labor‑intensive and slow. In contrast, RFID technology uses radio waves to read multiple tags concurrently. This method doesn’t require a visual connection. Consequently, RFID enables faster data collection and improved reliability. As a result, it has become a popular choice for modern asset management.
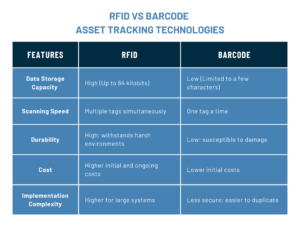
Read Comparison of Barcode Vs. RFID Asset Tracking – Pros & Cons of Two widely used Technologies>>
Types of RFID Asset Tracking
RFID asset tracking systems are available in three primary types, each suited to different applications and budgets:
-
Passive RFID
Passive RFID tags are the most commonly used type. Unlike active tags, passive tags lack an internal power source. Instead, they draw power from radio waves emitted by RFID readers. Therefore, they offer a cost-effective solution for many businesses. They are particularly suited for use cases where real-time location tracking is unnecessary. For instance, they automate physical asset verification. Additionally, they support check-in and check-out monitoring with minimal infrastructure.
-
Active RFID
Active RFID tags come with an internal battery that enables them to transmit data continuously. These tags are designed for tracking high‑value or critical assets in real time. They can track assets over longer distances. Although more expensive than passive tags, they provide continuous tracking and cover wider areas. Thus, they are essential when real‑time asset location is required.
-
Semi‑Passive RFID
Also known as battery‑assisted passive (BAP) RFID tags, these combine features of both active and passive tags. These tags include a battery to power certain functions. However, they still rely on the RFID reader’s signal for communication. This hybrid solution offers better performance than passive tags, while keeping costs lower than fully active tags.

White Paper
Automate recording of Asset check-in and checkout using RFID Technology. Download our latest white paper to learn how to implement and benefit from automation
White Paper
Discover how AssetCues automates asset verification and management in SAP, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. Learn more about our SAP Certified Solution!

RFID Asset Tracking Applications
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is highly versatile, offering a range of applications across various industries:
-
Automation of Physical Asset Verification
Manual asset verification is time‑consuming and error‑prone. RFID systems automate asset tracking by enabling the simultaneous scanning of multiple items. This can even occur through barriers. For example, during audits, an RFID reader can quickly confirm the presence of hundreds of assets. As a result, verification time is reduced from hours to minutes.
-
IT Asset Tracking
Organizations managing large inventories of IT equipment, like laptops and servers, benefit from RFID. They tag each asset with a unique identifier. This enables real-time monitoring of asset movement and usage. As a result, high‑value items are always accounted for, enhancing overall IT asset management. To see how RFID transforms IT asset management in real-world scenarios, read our Guide on Using RFID for IT Asset Tracking>>
-
Real‑Time Location Systems (RTLS) Using Active RFID
Active RFID tags are crucial for RTLS applications. These systems continuously track the location of assets in environments like hospitals, healthcare facilities, or large manufacturing plants. RTLS enables managers to monitor asset movement, quickly locate items, and optimize workflow efficiencies.
-
Tool Tracking
In industries where tools are frequently shared, such as construction or manufacturing, RFID tracking helps. It minimizes loss, prevents unauthorized usage, and optimizes tool utilization across teams.
-
RFID Medical Equipment Tracking
Healthcare facilities use RFID to track expensive and critical medical equipment. Automated tracking reduces downtime, improves patient care, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
Components of an RFID Asset Tracking System
Implementing an effective RFID asset tracking system requires understanding its key components:
-
RFID Asset Tracking Software
This software acts as the brain of the system and processes data collected by RFID readers. Additionally, it automates physical asset verification and maintains an up-to-date asset database. It also monitors asset movement and generates dashboards and reports. Moreover, a robust software solution integrates with existing enterprise systems. This way, it supports comprehensive and seamless asset monitoring.
-
RFID Asset Tags
RFID tags, affixed to each asset, consist of a microchip and an antenna. The microchip stores a unique identifier and other pertinent data. The antenna then transmits this information to the RFID reader. When selecting tags, consider factors like durability, cost, and asset requirements. For example, tags for metal objects may need specialized designs to prevent interference
-
RFID Hardware
This includes RFID readers and antennas.
Fixed Readers: Installed at strategic locations (e.g., doorways, loading docks) to capture asset movements and deter unauthorized transfers.
Mobile Readers: Handheld devices used for conducting physical audits or tracking assets across large areas.
The choice between fixed and mobile readers depends on your tracking needs and the operational environment.
Integration of the Asset Tracking System with Other Applications
To fully realize the benefits of RFID asset tracking, it is crucial to integrate the system with your existing software ecosystem. Key integrations include:
-
ERP Systems:
Connecting RFID data with ERP systems ensures asset information is synchronized. This synchronization spans finance, procurement, and operations, thereby enhancing decision-making.
White Paper
Discover how AssetCues automates asset verification and management in SAP, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. Learn more about our SAP Certified Solution!

White Paper
Discover how AssetCues automates asset verification and management in SAP, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and compliance. Learn more about our SAP Certified Solution!

-
ITSM/CMDB/ITAM:
For IT asset tracking, integration with ITSM, CMDB, and ITAM systems is crucial. It provides a unified view of IT resources, streamlining maintenance and lifecycle management.
White Paper
Learn best practices on Reconciling IT assets information with the Asset Register maintained in ERP! Download our white paper now!

White Paper
Learn best practices on Reconciling IT assets information with the Asset Register maintained in ERP! Download our white paper now!

-
HRMS:
Integrating with Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) facilitates tracking of assets assigned to employees, ensuring accountability and smoothing check‑in/check‑out processes.
RFID Asset Tracking Costs
The cost of an RFID asset tracking system varies based on several factors:
-
Type of RFID Tags:
Passive tags are generally less expensive, while active tags incur higher costs due to their internal power source.
-
Hardware:
RFID readers and antennas can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on capabilities and read range
-
Software and Integration:
Consider subscription fees for asset tracking software and any customization required to integrate with your existing platforms.
-
Maintenance:
Ongoing expenses for tag replacement, reader upkeep, and software updates should also be factored in.
While the initial investment may be higher compared to traditional methods, the long‑term savings from reduced labor justify the expense. Additionally, minimized asset loss and improved operational efficiency contribute to the overall value.
Get a Free Estimation of Implementing RFID Technology.
Contact our team to get a free quote for RFID Asset Tracking Implementation for your organisation.

Get a Free Estimation of Implementing RFID Technology
Contact our team to get a free quote for RFID Asset Tracking Implementation for your organization.

Key Benefits of RFID Asset Tracking
Implementing an RFID asset tracking system provides several critical benefits:
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Automated scanning significantly reduces the time required for asset verification while minimizing manual errors. RFID systems enable the simultaneous tracking of multiple items, streamlining audits and reconciliation processes.
- Real‑Time Visibility and Data Accuracy: RFID technology provides instant updates on asset location and status. As a result, it ensures records remain current and supports better decision-making. Moreover, it enables smarter resource allocation across departments.
- Enhanced Security and Loss Prevention: RFID systems detect unauthorized asset movement in real time. They instantly alert managers to potential threats or anomalies. Therefore, they help prevent theft and ensure high-value items are well protected.
- Cost Reduction and Long‑Term Savings: RFID automates asset tracking and reduces manual errors significantly. Consequently, it lowers labor costs and improves operational efficiency. Over time, it results in substantial long-term savings through optimized asset utilization.
- Support for Regulatory Compliance and Auditing: RFID systems provide accurate, real-time asset data consistently. Thus, they simplify compliance with regulatory standards. In addition, they streamline audits by generating detailed and reliable reports.
Challenges and Limitations of RFID Asset Tracking
Despite its numerous advantages, RFID asset tracking presents several challenges:
- Accurate Asset Database: RFID asset tracking starts with an accurate baseline inventory. This process requires coordination across teams and must be executed diligently.
- Initial Investment and Setup Costs: RFID tags, readers, and system integration involve significant upfront costs. Therefore, effective budget planning ensures alignment with the expected return on investment.
- Choosing the Right RFID Asset Tag: Metal, liquids, or interference can disrupt RFID signals. In such cases, use specialized tags or extra infrastructure to resolve signal issues.
- Integration and Compatibility Issues: Integrating with ERP or ITAM systems can be complex. As a result, custom integration work may be necessary to ensure seamless operation.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Operational Challenges: Perform regular maintenance to keep tags secure and readers functional. Hence, consistent upkeep is essential for sustaining long-term system performance.
- Selecting the Right Software and Implementation Partner: Choose dependable software and a capable implementation partner. This decision is critical to maximizing your RFID system’s overall value.
Future Trends & Innovations in RFID Asset Tracking
The RFID landscape is continuously evolving, and several emerging trends promise to further enhance its capabilities:
-
Advancements in RFID Technology:
- Miniaturization: RFID tags are becoming smaller and more discreet. Consequently, they work well for tracking small assets or where appearance matters.
- Dual‑Mode Tags: New tag designs now blend features of active and passive RFID technologies. As a result, they offer longer ranges and better data transmission—without the high cost.
-
Integration with IoT and AI:
- As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, RFID systems are increasingly integrated with IoT platforms. Coupled with artificial intelligence (AI), these systems can provide predictive analytics for maintenance scheduling, asset utilization, and security threat detection. AI‑driven insights enable organizations to make data‑driven decisions and optimize asset performance.
-
Enhanced Data Analytics:
- Future RFID systems will not only track asset locations but also provide comprehensive insights through advanced data analytics. This helps organizations optimize operations and predict potential failures. Moreover, it enhances efficiency by revealing detailed asset utilization patterns.
According to recent market research on RFID technology (Source: Fortune Business Insights), the global RFID market will reach USD 37.71 billion by 2032. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.9% from 2025 to 2032. This growth is driven by rising demand across logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors.
Best Practices for Implementing RFID Asset Tracking
To ensure a successful RFID asset tracking deployment, adhere to the following best practices:
-
Assess Business Needs and Objectives:
Clearly define your goals—reducing audit time, preventing loss, or enhancing security. Then, identify the most critical assets you need to track.
-
Select the Right Hardware and Technology:
Choose RFID tags, readers, and software that suit your operational environment. Consider factors such as read range, durability, cost, and compatibility with existing systems. For instance, passive RFID is typically cost‑effective for stationary assets, while active RFID is ideal for high‑value, mobile assets.
Also, read our blog on “Asset Tracking Tags: Key Factors in Selecting the Best Tag” -
Strategic Tag and Reader Placement:
Plan the installation of RFID readers and tag placement to ensure maximum coverage with minimal interference. Place fixed readers at high-traffic areas or choke points. Use mobile readers for audits and on-site tracking.
-
Training Staff and Ensuring User Adoption:
Provide comprehensive training on proper tag application and the use of asset tracking software. A well‑trained team will maximize the benefits of the system and reduce errors.
-
Regular System Audits and Performance Optimization:
Establish routine audits and maintenance schedules. Additionally, regularly review data accuracy, inspect hardware, and update software to ensure the RFID system consistently meets your business requirements.
Conclusion
RFID asset tracking represents a major advancement in asset management technology. To begin with, it automates tracking and provides real-time data. Moreover, it integrates seamlessly with enterprise systems. Consequently, businesses manage assets more efficiently and securely. Throughout this guide, we examined the basics of RFID asset tracking. In particular, we explained how the technology works and the types available. Furthermore, we highlighted real-world applications, key components, and integration methods. Lastly, we discussed costs, benefits, challenges, and emerging trends that shape the future of RFID tracking.
Whether you manage IT equipment, high-value tools, or medical devices, RFID asset tracking enhances your operations. It boosts accuracy, reduces labor costs, and strengthens security. Additionally, RFID solutions adapt seamlessly to your unique business needs.
So, why wait? Embrace the future of asset management with a solution tailored for measurable results.
Explore our solution or schedule a demo today to see how RFID can elevate your efficiency. AssetCues benefitted organizations in saving more than 70% time and cost in performing physical verification of assets through RFID Asset Tracking.
Stay ahead in a competitive market by investing in technology that tracks your assets and drives long-term savings.
FAQs
Q. What is RFID asset tracking?
A. RFID asset tracking is a method that uses radio frequency identification tags to monitor assets automatically. These tags store asset information and enable real-time visibility, reducing human error and improving asset utilization.
Q. How does RFID asset tracking work?
A. The system involves attaching RFID tags to assets, which are read by fixed or handheld RFID readers. The data is then processed by software to provide instant updates on asset location and movement.
Q. What industries benefit most from RFID asset tracking systems?
A. Industries like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and construction benefit most from RFID systems. These sectors require real-time asset visibility and fast, accurate audits. Moreover, they manage high volumes of movable assets daily. Therefore, RFID becomes an ideal solution for improving control and efficiency.
Q. What types of assets can be tracked using RFID technology?
A. RFID can track physical assets like tools, machinery, IT equipment, vehicles, documents, and returnable packaging. It’s effective across diverse environments, whether indoor warehouses or outdoor sites.
Q. How much does RFID asset tracking cost?
A. Costs vary based on tag type, infrastructure, and software requirements. Passive RFID systems are affordable, while active systems with long-range capabilities and advanced features cost more.
Contact our team for a customized quote on implementing RFID asset tracking in your organization
Talk to our team for a quote for implementing RFID Asset tracking in your organization
Contact our team for a customized quote on implementing RFID asset tracking in your organization
Talk to our team for a quote for implementing RFID Asset tracking in your organization




